Essential oils have gained immense popularity in recent years for their natural and aromatic properties. From lavender to tea tree, these oils are believed to offer a range of therapeutic benefits. However, there is a growing concern that essential oils may not be as skin-friendly as we once thought. In this article, we will explore the potential side effects of essential oils on the skin and shed light on the precautions to take when using them.
The Complex Nature of Essential Oils
Essential oils are highly concentrated extracts derived from plants, containing volatile compounds that contribute to their distinct aroma and therapeutic properties. While these natural compounds can offer benefits, they also possess complex chemical compositions that can interact with the skin in various ways. It is essential to recognize that not all essential oils are suitable for direct application to the skin, as they can cause adverse reactions in certain individuals.
Skin Sensitization and Allergic Reactions
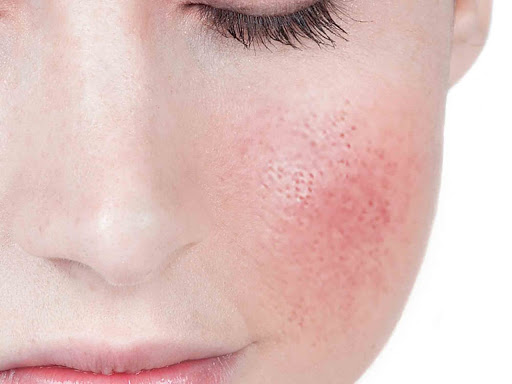
One of the most common concerns associated with essential oils is skin sensitization and allergic reactions. Some essential oils, such as citrus oils (e.g., lemon, bergamot), contain phototoxic compounds that can cause skin irritation, redness, and even blistering when exposed to sunlight. Additionally, individuals with sensitive skin or pre-existing allergies may experience allergic contact dermatitis when using certain essential oils, resulting in itching, rash, or hives.
Irritation and Disruption of the Skin Barrier
Essential oils, even those considered generally safe, can cause skin irritation, especially when used undiluted or in high concentrations. The potent nature of essential oils can disrupt the skin barrier, leading to dryness, redness, and increased sensitivity. This disruption can compromise the skin’s ability to retain moisture and protect against external aggressors, making it more susceptible to environmental damage.
Essential Oils and Acne Breakouts
Despite their popularity in skincare, some essential oils can exacerbate acne breakouts. Certain oils, such as coconut oil and some members of the mint family, are comedogenic, meaning they can clog pores and contribute to the formation of blackheads and whiteheads. Individuals with acne-prone or oily skin should exercise caution when incorporating essential oils into their skincare routine.
Photosensitivity and Sun Damage
As mentioned earlier, several essential oils contain phototoxic compounds that can increase the skin’s sensitivity to sunlight. When applied topically and exposed to UV rays, these oils can lead to severe sunburn, pigmentation changes, and long-term sun damage. It is critical to avoid sun exposure after using phototoxic essential oils or to use adequate sun protection measures to minimize the risk.
Precautions and Safe Usage
To minimize the potential risks associated with essential oils, it is essential to observe certain precautions and practice safe usage:
- Always perform a patch test before applying any essential oil to your skin.
- Dilute essential oils properly by mixing them with carrier oils, such as jojoba or almond oil.
- Follow recommended dilution ratios and usage guidelines provided by reputable sources.
- Be cautious when using essential oils on sensitive areas, such as the face or genitals.
- Store essential oils in a cool, dark place away from direct sunlight.
- Consider consulting a qualified aromatherapist or dermatologist for personalized advice.

While both skin sensitization and allergic reactions can occur in response to essential oil usage, they are distinct processes with different underlying mechanisms.
Skin Sensitization:
Skin sensitization is an acquired immune response that develops over time with repeated exposure to a particular substance. In the context of essential oils, it occurs when an individual’s immune system recognizes specific components within the oil as foreign or harmful. As a result, the immune system mounts an immune response, leading to inflammation and skin reactions.
The process of skin sensitization typically involves three stages:
a) Sensitization Phase: During the initial exposure, the immune system identifies the essential oil components as potential allergens. The immune system activates specific immune cells called T cells, which are responsible for recognizing and remembering the allergen.
b) Latent Phase: After the initial exposure, there is typically no immediate visible reaction. However, the immune system has now developed memory T cells specific to the essential oil allergen.
c) Elicitation Phase: Upon subsequent exposure to the same essential oil, the immune system recognizes the allergen and triggers an immune response. This response results in skin symptoms such as itching, redness, rash, or blistering.
Skin sensitization is not an immediate reaction and usually requires multiple exposures to the allergen before symptoms become apparent. It is important to note that skin sensitization can occur even with essential oils that are generally considered safe for most individuals.
Allergic Reactions:
Allergic reactions to essential oils are immediate responses mediated by the immune system. They occur when an individual’s immune system overreacts to a specific allergen present in the oil. Unlike skin sensitization, allergic reactions can occur with the first exposure to the allergen.
In the case of essential oils, allergic reactions can manifest as allergic contact dermatitis. This condition occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with an allergenic substance, triggering an immune response. Symptoms may include redness, itching, swelling, hives, or blisters.
It is important to note that individuals can develop allergies to specific essential oils or their components, even if they have not previously experienced any adverse reactions. Allergic reactions tend to be more immediate and can occur even with a single exposure.
It’s worth mentioning that some essential oils are more likely to cause skin sensitization or allergic reactions due to their chemical composition. For example, citrus oils (e.g., lemon, bergamot) containing furanocoumarins can cause phototoxicity, leading to skin reactions when exposed to sunlight.
To minimize the risk of skin sensitization and allergic reactions, it is crucial to perform a patch test before using any essential oil and to follow recommended dilution ratios and usage guidelines.
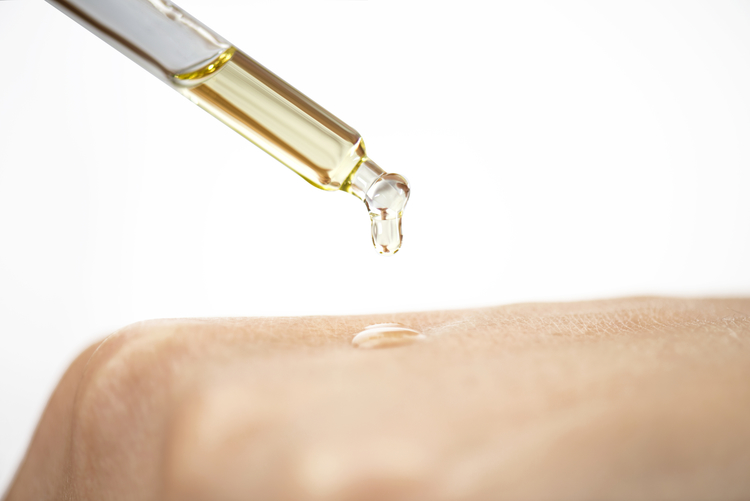

While essential oils can offer various benefits, it is crucial to be aware of their potential side effects on the skin. Skin sensitization, irritation, disruption of the skin barrier, acne breakouts, photosensitivity, and allergic reactions are just a few of the concerns associated with these potent extracts. By understanding the risks and taking necessary precautions, individuals can enjoy the therapeutic properties of essential oils while minimizing the potential havoc they may wreak on their skin.